In various industries – particularly within healthcare, manufacturing, and construction sectors – employees often find themselves engaging in manual handling tasks. These tasks can range from lifting and moving heavy items to repetitive motions that, without proper technique, can lead to serious injuries. This article delves into the best practices for ensuring safety during these critical activities, promoting a healthy workplace environment.
Table of Contents
Understanding Manual Handling
Before diving into techniques and tips, it’s essential to understand what manual handling encompasses. It refers to any activity requiring the use of force by a person to lift, lower, push, pull, carry, or otherwise move, hold, or restrain any object or person. Adopting safe manual handling strategies is crucial in mitigating associated risks, ensuring employee safety, and maintaining optimal levels of productivity.
Risks Associated with Manual Handling
Manual handling can pose significant risks when performed incorrectly. These include musculoskeletal disorders, back injuries, muscle strains, and in more severe cases, long-term disability. Certain sectors face unique challenges – the manual handling hazards in aged care, for instance, involve moving residents, repetitive tasks, and working in constrained spaces, often leading to increased occupational hazards.
Best Practices for Safe Manual Handling
- Proper Training and Education: Comprehensive training programs should be a prerequisite for all staff members involved in manual handling. These programs need to cover risk assessment, safe handling techniques, and the use of mechanical aids.
- Use of Mechanical Aids: Wherever possible, use mechanical aids (like wheelchairs, adjustable beds, and hoists) to minimize physical strain. Understanding and utilizing these aids correctly is crucial in preventing overexertion and injuries.
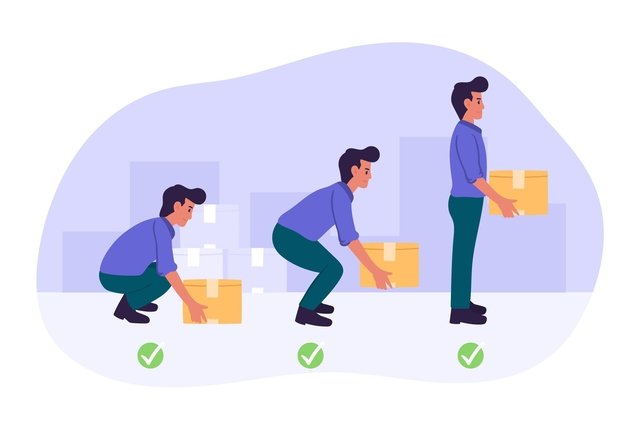
- Correct Lifting Techniques: Adopt the “LITE” (Load, Individual, Task, Environment) technique for risk assessment before proceeding with any task. Remember to:
- Keep the load close to the waist to reduce the load on the back.Maintain a stable position with feet apart, providing a balanced and solid base for lifting.Avoid bending the back or twisting when lifting – instead, bend the knees.
- Move smoothly without jerking, as this can make it harder to control the weight and increase the risk of injury.
- Tailored Strategies for Specific Work Environments: Strategies should cater to the unique needs of various sectors. For instance, healthcare and aged care workers require specialized training to handle residents properly, keeping in mind their comfort and dignity, besides the safety of both parties.
- Regular Risk Assessments: Conducting regular risk assessments identifies potential hazards before they cause harm. These assessments should examine the nature of the task, load, working environment, and individual capability.
- Encouraging a Culture of Safety: Foster a workplace environment where employees feel comfortable voicing concerns related to manual handling. Prompt reporting leads to quick action and helps prevent escalation of any identified issues.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Workplace safety is an evolving process – regularly review and refine manual handling policies and practices. Solicit feedback from staff, and be open to adopting new practices or technologies that could contribute to a safer work environment.
Adhering to the best practices for safe manual handling is not just a regulatory requirement, but also a moral obligation by employers to ensure the welfare of their staff
It demands a proactive approach, from offering educational resources and correct training to investing in appropriate equipment. By embedding these practices into the organisational culture, companies can significantly reduce the risk of injuries, boost employee morale, and by extension, enhance productivity. Remember, a commitment to safety is a commitment to overall excellence.